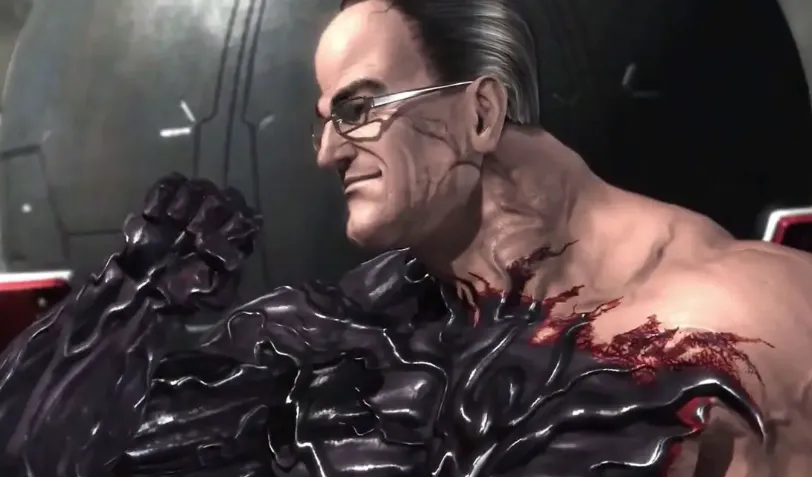
Nanomachines, Son refers to a meme from the game Metal Gear Rising: Revengeance. It highlights the character Senator Armstrong’s speech about nanotechnology.
Nanomachines, Son, a popular internet meme, originates from the game Metal Gear Rising: Revengeance. The phrase is attributed to Senator Armstrong, a character in the game, during a memorable speech about the power and influence of nanotechnology. This meme has gained widespread recognition due to its humorous and impactful nature.
Fans of the game and meme enthusiasts often use it to reference exaggerated or overly powerful technology. The phrase encapsulates the futuristic and often dystopian themes in many video games and science fiction narratives. Its popularity demonstrates the enduring appeal of memorable lines and characters in gaming culture.
Nanomachines’s Bio
| Attribute | Details |
|---|---|
| Name | Nanomachines |
| Scientific Classification | Nanoscale Molecular Machines |
| Developed by | Multiple researchers and organizations worldwide, prominent in fields like nanotechnology, medicine, and robotics |
| Typical Scale | 1–100 nanometers |
| Body Measurements | Varies; can be as small as individual molecules (1-100 nm) |
| Weight | Negligible, typically measured in atomic mass units |
| Gender | Not applicable |
| Sexual Orientation | Not applicable |
| Functionality | Molecular machines, transport systems, sensing, repair, and catalysis at nanoscale |
| Material Composition | Primarily composed of organic molecules, polymers, metals, or composite nanostructures |
| Body Type | Molecular structures, often designed in specific shapes for functionality |
| Primary Applications | Medicine (drug delivery, diagnostics), environmental (pollution cleanup), electronics, materials science |
| Key Developers | Dr. Richard Feynman (early concepts), Dr. Eric Drexler (molecular nanotechnology), and modern nanotechnology researchers worldwide |
| Net Worth | Not directly applicable; value is instead measured by funding and industry impact |
| Current Status | Active area of research, with some applications in clinical trials, industrial use, and further development underway |
Who Are Nanomachines?
“Nanomachines” are a groundbreaking achievement in nanotechnology, representing the field’s strides in engineering machines on an atomic or molecular scale. Unlike conventional machines, nanomachines operate at a level invisible to the human eye, often measuring between 1-100 nanometers. They are designed to perform specific, predetermined functions at this minute scale, such as moving, transporting molecules, sensing environmental changes, or even assembling molecular structures autonomously. The idea was first theoretically explored by physicist Richard Feynman in his 1959 talk “There’s Plenty of Room at the Bottom,” and later by Dr. Eric Drexler, who further advanced concepts in molecular nanotechnology.
Nanomachines operate based on their carefully designed structures, which enable them to interact with other molecules and environments at the nanoscale. Their applications are incredibly diverse, spanning fields like medicine, environmental science, and electronics. In medicine, nanomachines have shown promise in targeted drug delivery systems, allowing drugs to be delivered directly to diseased cells, thus minimizing side effects. In cancer treatments, for instance, nanomachines can carry chemotherapeutic agents directly to tumors, sparing healthy tissues and reducing toxicity. Additionally, nanomachines are also being explored for their potential in diagnostic procedures, providing real-time insights at a cellular level, and potentially offering rapid diagnostics for diseases like cancer and infectious diseases.
In the environment, nanomachines have potential in pollution control, where they can be programmed to neutralize pollutants at a molecular level. For instance, specialized nanomachines could target and break down specific pollutants in water sources, offering a promising tool for environmental cleanup. In electronics, nanomachines are also being applied to create more efficient and smaller devices, advancing fields like quantum computing and energy storage.
Despite the tremendous potential, nanomachines also raise ethical and safety concerns, especially when used within biological systems. Issues of toxicity, long-term impacts, and environmental accumulation are still under investigation. Additionally, as nanomachines become more sophisticated, they bring up questions related to biosecurity, particularly if self-replicating nanomachines become feasible in the future. Today, research continues to push the boundaries of what nanomachines can achieve, making it one of the most exciting and revolutionary fields in technology and science.
Introduction To Nanomachines
Nanomachines are tiny devices that operate at the molecular level. These machines can perform tasks in microscopic environments. They have the potential to revolutionize various fields, including medicine and technology. In this section, we will explore what nanomachines are and their historical development.
What Are Nanomachines?
Nanomachines are minuscule devices, typically smaller than a cell. They can manipulate matter at the atomic scale and can include motors, sensors, and other functional components. They operate in environments too small for traditional machines.
Nanomachines can be made from various materials, including proteins and synthetic molecules. They are designed to perform specific tasks, such as drug delivery or tissue repair. Their potential applications are vast and varied.
Historical Development
| Year | Development |
| 1959 | Richard Feynman introduces the concept of nanotechnology. |
| 1981 | The first scanning tunneling microscope was developed. |
| 1991 | Carbon nanotubes were discovered, paving the way for nanomachines. |
| 2000s | First, functional nanomachines were created and tested. |
Richard Feynman first proposed the concept of nanotechnology in 1959. He envisioned machines that could manipulate individual atoms. The development of the scanning tunneling microscope in 1981 was a significant milestone. This tool allowed scientists to visualize and manipulate atoms directly.
Another breakthrough was the discovery of carbon nanotubes in 1991. These structures provided a new material for building nanomachines. By the 2000s, researchers had created the first functional nanomachines, which demonstrated the feasibility of nanotechnology.
Mechanisms Of Nanomachines
Nanomachines are tiny devices that operate on a microscopic scale. They have the potential to revolutionize medicine, manufacturing, and technology. Understanding their mechanisms is essential for harnessing their power.
Basic Principles
The basic principles of nanomachines involve converting energy into motion. This motion is achieved through various mechanisms, such as chemical reactions, electrical impulses, or magnetic fields. These machines mimic biological systems to perform specific tasks.
- Chemical Reactions: Nanomachines can use chemical reactions to move and work.
- Electrical Impulses: They can be powered and controlled using electrical signals.
- Magnetic Fields: Magnetic fields can guide and direct their movement.
These principles allow nanomachines to operate in diverse environments.
Key Components
Nanomachines consist of several key components. Each component plays a crucial role in their function.
| Component | Function |
| Power Source | Provides energy for the machine’s operations. |
| Sensors | Detects environmental conditions and changes. |
| Actuators | Converts energy into mechanical motion. |
| Control Units | Directs and regulates the machine’s actions. |
Each component must work together seamlessly. This coordination ensures the efficiency and effectiveness of nanomachines.
Nanomachines In Medicine

Nanomachines are tiny devices that can work at the molecular level. They hold great promise for the field of medicine. They can perform tasks that are difficult for larger machines, and their potential uses are vast and revolutionary.
Targeted Drug Delivery
Targeted drug delivery is a significant benefit of nanomachines. These machines can deliver drugs directly to diseased cells, minimizing damage to healthy cells and leading to fewer side effects for patients.
Nanomachines can carry drugs through the bloodstream. They release the medicine only at the target site, ensuring higher treatment efficiency.
Here are some key benefits:
- Reduced side effects
- Improved drug efficiency
- Minimized damage to healthy cells
Cancer Treatment
Nanomachines can enhance cancer treatment by identifying and destroying cancer cells. Traditional treatments often harm healthy cells, but nanomachines can provide a more precise approach.
For example, nanomachines can be equipped with sensors. These sensors detect cancer cells. Once detected, the nanomachines can release drugs directly into the cancerous cells, effectively killing them.
Advantages of using nanomachines for cancer treatment include:
- Targeted destruction of cancer cells
- Less harm to healthy tissues
- Higher success rates
Here is a comparison table of traditional vs. nanomachine cancer treatments:
| Traditional Treatment | Nanomachine Treatment |
| Non-specific targeting | Specific targeting |
| More side effects | Fewer side effects |
| Lower efficiency | Higher efficiency |
Nanomachines have the potential to change how we treat many diseases. They offer a new level of precision and effectiveness in medicine.
Nanomachines In Technology

Nanomachines are transforming various industries. They can manipulate materials at an atomic level. This unique ability makes them highly valuable in technology. Below are some exciting applications of nanomachines in technology.
Electronics And Computing
Nanomachines are revolutionizing electronics and computing. They allow for the creation of smaller, more efficient devices. Smartphones, laptops, and other gadgets are becoming more powerful and compact.
- Enhanced battery life
- Faster processing speeds
- Higher storage capacity
Nanomachines help in developing quantum computers. These computers can perform complex calculations quickly. They are expected to solve problems that are unsolvable today.
Nanocircuits are another innovation. They use nanomachines to create incredibly small electronic circuits, which helps produce more energy-efficient and faster electronic devices.
Environmental Applications
Nanomachines are also useful in environmental applications. They can detect and clean pollutants at a molecular level, leading to cleaner air and water.
- Water purification
- Air quality monitoring
- Soil decontamination
In water purification, nanomachines remove harmful substances, ensuring safe drinking water. They can also detect toxins and pollutants in real-time.
Nanomachines help in air quality monitoring. They can identify pollutants and harmful gases, which allows for timely action to improve air quality.
For soil decontamination, nanomachines target and break down hazardous chemicals, making the soil safe for agriculture and other uses.
Challenges And Limitations
Nanomachines promise revolutionary changes in medicine, manufacturing, and technology. Yet, they face significant challenges and limitations that hinder their development and implementation. Below, we explore the key hurdles.
Technical Hurdles
Building nanomachines requires extreme precision and advanced materials. They must operate at the molecular level. This scale presents unique challenges. Engineers need tools to manipulate atoms and molecules. Current technology may need to be
improved.
Another issue is powering nanomachines. They need a reliable energy source, but traditional batteries are too large. Innovative solutions like biochemical energy are under research. Communication between nanomachines is also complex. They must coordinate actions seamlessly.
| Technical Challenge | Description |
| Precision Engineering | Requires tools to manipulate atoms and molecules. |
| Power Supply | Needs tiny, reliable energy sources. |
| Communication | Must coordinate actions seamlessly. |
Ethical Considerations
Nanomachines raise significant ethical questions. Who controls these powerful tools? Potential misuse is a major concern. They could be weaponized or used for surveillance. There must be strict regulations.
Privacy is another issue. Nanomachines could collect personal data, raising concerns about data security and consent. Society needs to address these ethical dilemmas.
- Control and misuse
- Weaponization
- Surveillance
- Privacy and data security
Creating guidelines and regulations is crucial. These will ensure nanomachines benefit humanity. Without ethical oversight, the risks outweigh the potential benefits.
Current Research And Innovations
Nanomachines are tiny robots, smaller than a grain of sand. Scientists are exploring their potential, which could change many fields. Let’s explore current research and innovations in nanomachines.
Leading Projects
Many universities and companies are working on nanomachines. Below are some leading projects:
| Project | Institution | Focus Area |
| Nanobot Drug Delivery | MIT | Medicine |
| Micro Swimmers | Stanford University | Environmental Cleanup |
| Smart Dust | UC Berkeley | Surveillance |
MIT is leading in nanobot drug delivery. They aim to deliver drugs directly to diseased cells. This could make treatments more effective.
Stanford University is exploring microswimmers. These tiny machines clean pollutants from water, helping to keep our environment clean.
UC Berkeley is developing smart dust. These are tiny sensors. They can monitor environments for security purposes.
Future Directions
The future of nanomachines looks bright. Here are some possible future directions:
- Medical Nanobots: Nanobots could perform surgeries. They could repair tissues at a cellular level.
- Environmental Applications: Nanomachines could clean up oil spills. They could also help in recycling.
- Industrial Uses: In factories, nanomachines could build products. They could work on a very small scale.
Researchers hope to see these advancements soon. The impact could be huge, as the tiny nanomachines could bring big changes.
Potential Risks
Nanomachines offer incredible benefits, yet they come with potential risks. Understanding these risks helps us use nanotechnology safely. Here, we explore the main concerns.
Health Risks
Nanomachines could impact human health. They may enter the body through inhalation, ingestion, or skin contact. Their tiny size allows them to reach organs and tissues.
- Toxicity: Nanoparticles might be toxic to cells.
- Inflammation: They could cause inflammation in tissues.
- Cell Damage: Some nanomachines might damage cells or DNA.
To minimize health risks, scientists conduct thorough tests. They monitor how nanomachines interact with the human body.
Environmental Impact
Nanomachines might affect the environment. They can enter soil, water, and air, causing unforeseen changes.
- Water Contamination: Nanoparticles could contaminate water sources.
- Soil Health: They may alter soil composition and harm plants.
- Air Quality: Tiny particles can affect air quality, impacting health.
Environmental studies are crucial. Researchers analyze nanomachines’ impact on ecosystems. They seek ways to mitigate negative effects.
Nanomachines Net Worth and Market Value
While nanomachines do not have a “net worth” in the traditional sense, the nanotechnology market, which includes the development and application of nanomachines, has seen substantial investment over the years. Funding and market value have grown as the applications of nanomachines span healthcare, manufacturing, energy, and environmental sectors.
| Year | Global Nanotechnology Market Value | Primary Sectors for Investment | Growth Drivers |
|---|---|---|---|
| 2018 | $1.2 billion | Medicine, Electronics, Environmental Remediation | Advancements in nano-medicine and electronics |
| 2019 | $1.6 billion | Drug Delivery Systems, Water Purification, Smart Electronics | Increasing healthcare applications |
| 2020 | $2 billion | Diagnostic Tools, Electronics, Environmental Cleanup | COVID-19 diagnostics and treatment research |
| 2021 | $2.5 billion | Cancer Therapy, Quantum Computing, Renewable Energy | Rising demand in medical and energy sectors |
| 2022 | $3 billion | Precision Medicine, Wearable Technology, Industrial Catalysts | Expansion of nano-enabled devices |
| 2023 | $3.5 billion | Medical Devices, Sensors, Bio-nanotechnology | Increased funding for biotech and electronics |
Conclusion
Nanomachines are revolutionizing technology and medicine. Their potential is enormous, from targeted drug delivery to environmental cleanup. As research progresses, nanomachines will become integral to solving global challenges. Stay informed and embrace the future with nanotechnology advancements. The next big leap in innovation is just around the corner.
Read Also About: Garand Thumb Wife
